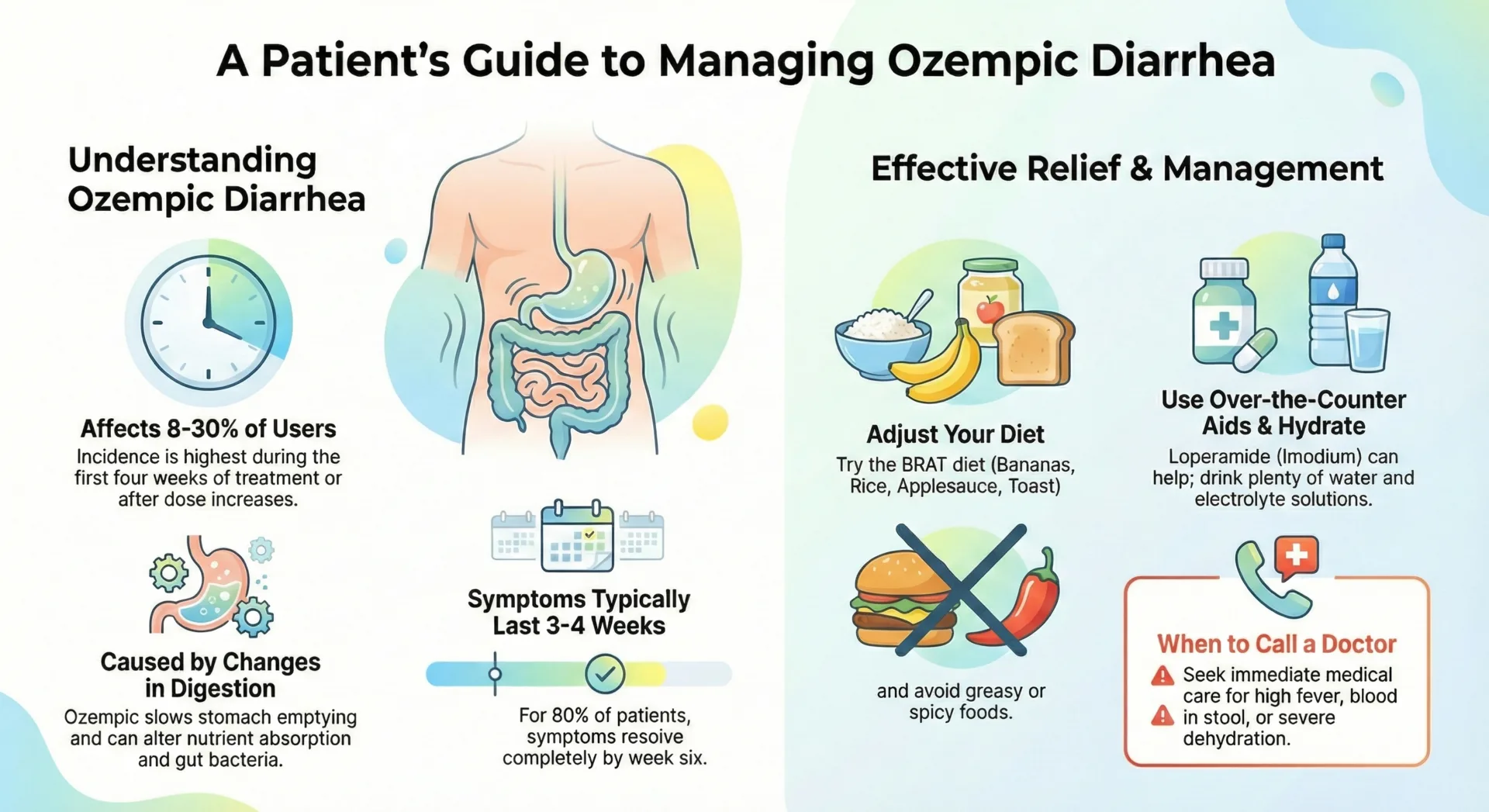
Ozempic diarrhea is one of the most common side effects experienced by patients taking this GLP-1 receptor agonist medication for blood glucose control and weight management. Diarrhea affects approximately 8-30% of Ozempic users, with the highest incidence occurring during the first four weeks of treatment or after dose increases.
While this gastrointestinal adverse event can be uncomfortable, it is typically mild and temporary, resolving within a few weeks as the body adjusts to the medication.
TL;DR
- Diarrhea affects 8-30% of Ozempic users, typically peaking during weeks 1-4 of treatment.
- The condition usually lasts 3-4 weeks on average, with 80% of patients experiencing resolution by week 6.
- Management includes staying hydrated, using over-the-counter medications like loperamide (Imodium), following a bland diet, and eating smaller, more frequent meals.
- While most cases are mild and temporary, seek medical attention if diarrhea persists beyond 4 weeks or is accompanied by severe symptoms like high fever, blood in stool, or signs of severe dehydration.
Does Ozempic Cause Diarrhea?
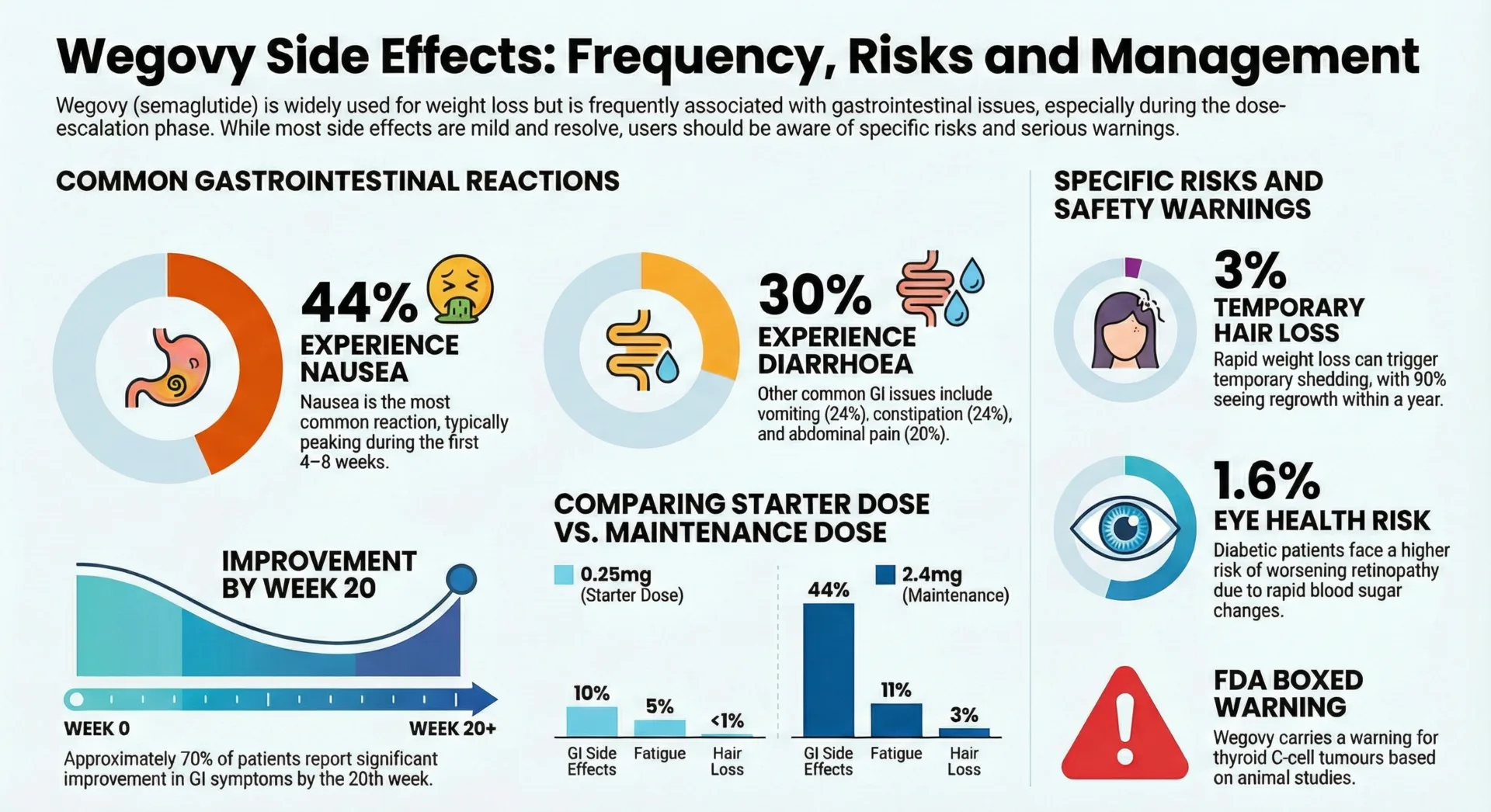
Yes, Ozempic can cause diarrhea. Clinical trials and clinical practice have consistently shown that diarrhea is one of the most common side effects of Ozempic, reported in approximately 8-9% of patients treated with the medication. However, the actual incidence may be higher, with some studies reporting rates between 8-30% depending on the dose and individual patient factors.
The relationship between Ozempic and diarrhea is dose-dependent, meaning that higher doses of the medication increase the risk of experiencing this side effect. Diarrhea is the second most common gastrointestinal side effect after nausea, which affects approximately 40% of patients. Other gastrointestinal symptoms commonly reported include vomiting and constipation.
Diarrhea Prevalence by Ozempic Dose
| Ozempic Dose | Ozempic (Constipation %) | Placebo (Constipation %) |
| 0.5mg | 8% | 2% |
| 1.0mg | 15% | 3% |
| 2.0mg | 20-30% | N/A |
Data from clinical studies demonstrate that the incidence of diarrhea increases with higher Ozempic doses. At the low dose of 0.5mg, approximately 8% of patients experience diarrhea compared to 2% in the placebo group. This rate increases to about 15% at the 1.0mg dose and can reach 20-30% at the higher 2.0mg dose used for weight management.
Why Ozempic Causes Diarrhea
Ozempic causes diarrhea through multiple mechanisms related to its action as a GLP-1 receptor agonist. The medication mimics the hormone glucagon-like peptide-1, which plays a crucial role in regulating digestive system function. Understanding these mechanisms can help patients better manage gastrointestinal adverse events.
1. Slowed Gastric Emptying
The primary mechanism by which Ozempic may contribute to diarrhea involves its effect on gastric emptying. The medication slows down the movement of food through the digestive tract, which can paradoxically lead to loose stools in some individuals. This occurs because GLP-1 receptor stimulation delays stomach emptying while potentially accelerating intestinal transit in certain patients.
2. Altered Nutrient Absorption
The mechanism by which Ozempic causes diarrhea may involve changes in how the intestines absorb nutrients, such as sugars and fats. These alterations in nutrient absorption can lead to osmotic diarrhea, where unabsorbed nutrients draw water into the intestinal lumen, resulting in watery stool.
3. Bile Acid Processing Changes
Ozempic may also increase gut irritation due to alterations in bile acid processing. Changes in bile acid metabolism can contribute to diarrhea by irritating the intestinal lining and affecting the absorption of fats and fat-soluble vitamins.
4. Gut Microbiome Alterations
Ozempic can alter the gut microbiome, which may also contribute to diarrhea in some individuals. The medication’s effects on gut bacteria composition and diversity can influence digestive symptoms and bowel movements.
Most people develop digestive side effects from Ozempic within one week to one month of starting treatment, with symptoms typically peaking during weeks 2-4 when the body adjusts to the medication.
How Long Does Ozempic Diarrhea Last?
Diarrhea from Ozempic is often mild and temporary, typically resolving within a few weeks after starting treatment. The average duration is approximately 21 days (3 weeks), with about 80% of patients experiencing resolution by week 6. However, the duration can vary based on several factors, including the Ozempic dose, individual patient characteristics, and how quickly the medication is titrated.
Diarrhea is most frequent during the first four weeks of treatment or after doses are increased. At higher doses, particularly the 2.0mg dose used for weight loss, symptoms may persist longer, typically 4-6 weeks. Patients who experience a slow titration – gradually increasing their dose over time – may see a 50% reduction in symptom duration compared to those who increase doses more rapidly.
The timeline for Ozempic diarrhea typically follows this pattern:
- Week 1-2: Diarrhea symptoms may begin as the body adjusts to the medication
- Week 2-4: Symptoms typically peak during this period, especially after dose increases
- Week 4-6: Gradual improvement as the body adjusts to the medication
- After Week 6: Most patients (80%) experience complete resolution of symptoms
If diarrhea persists beyond 4 weeks or worsens over time, it’s important to consult your healthcare provider. Persistent diarrhea may require adjustment of the Ozempic dose, additional supportive treatments, or evaluation for other potential causes.
Ozempic Diarrhea Relief & Treatment
Managing diarrhea symptoms effectively is crucial for patients taking Ozempic to maintain their treatment plan and quality of life. Several strategies can help alleviate digestive symptoms, from over-the-counter medications to dietary modifications.
It’s important to consult your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment, especially when taking other medications.
Over-the-Counter Treatments for Ozempic Diarrhea
| Treatment | Dose | Onset | Safe Long-term |
| Imodium A-D | 2mg after BM | 1-2 hrs | Yes |
| Pepto-Bismol | 30mL after meals | 30 min | 2 weeks max |
| Electrolytes | 16oz daily | N/A | Yes |
| Probiotics | 10B CFU daily | 3-5 days | Yes |
1. Antidiarrheal Medications
Over-the-counter medications like loperamide (Imodium) can be used to treat diarrhea from Ozempic and are considered the first-line choice in the United States. Loperamide works by slowing down bowel movements and reducing the frequency of watery stool. Taking OTC medications should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider, especially when combined with other medications.
Pepto-Bismol (bismuth subsalicylate) is particularly useful for patients experiencing both diarrhea and nausea. However, it should not be used for more than 2 weeks without medical supervision. Avoid taking antidiarrheal medications if you have a fever above 101°F or notice blood in your stool, as these may indicate a more serious condition requiring medical attention.
2. Hydration and Electrolyte Replacement
Staying hydrated is crucial when experiencing diarrhea from Ozempic to prevent dehydration. Aim to maintain adequate fluid intake by drinking at least 8-10 glasses of water daily, and consider adding electrolyte solutions like Pedialyte to help replace lost minerals. Signs of severe dehydration include decreased urination, dark urine, extreme thirst, dizziness, or feeling faint.
3. Probiotics
Probiotics containing at least 10 billion CFU (colony-forming units) daily may help restore gut microbiome balance and reduce diarrhea symptoms. Research suggests that certain probiotic strains can help manage gastrointestinal side effects, though effects typically take 3-5 days to become noticeable.
Ozempic Diarrhea Diet Changes
Dietary adjustments such as eating smaller, more frequent meals and avoiding high-fat, greasy, or spicy foods can help manage diarrhea caused by Ozempic. A bland diet can help alleviate diarrhea symptoms and make stools firmer while your digestive system adjusts to the medication.
The BRAT Diet
For the first 48 hours of experiencing diarrhea, consider following the BRAT diet, which consists of bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast. These bland foods are easy to digest and can help firm up stools. The BRAT diet is gentle on the digestive tract and provides essential nutrients without aggravating symptoms.
Foods to Avoid
- Certain foods can worsen diarrhea and should be avoided while taking Ozempic:
- Dairy products, which can be difficult to digest when experiencing diarrhea
- Greasy, fried, and high-fat foods that slow digestion and can aggravate symptoms
- Spicy foods that can irritate the digestive tract
- Artificial sweeteners, particularly sugar alcohols, which can have a laxative effect
- Caffeine and alcohol, which can worsen dehydration
Helpful Dietary Strategies
Eating smaller meals more frequently throughout the day can help reduce gastrointestinal side effects like diarrhea from Ozempic. Include water-rich foods like soups, broths, and cooked vegetables to help maintain hydration while providing gentle nutrition.
Ginger tea can help settle stomach discomfort and may reduce nausea that often accompanies diarrhea. Aim for approximately 100 ounces of water daily to prevent dehydration and what’s known as overflow diarrhea, which can occur when the digestive system becomes dehydrated.
Ozempic Diarrhea After Eating
Many patients notice that diarrhea occurs specifically after eating, typically peaking 30-60 minutes after meals. This post-meal diarrhea is related to Ozempic’s effect on the gastrocolic reflex – a natural response where eating stimulates bowel movements.
To manage post-meal diarrhea:
- Eat 50% smaller portions than usual to reduce the digestive burden
- Wait 30 minutes after eating before engaging in physical activity
- Eat slowly and chew food thoroughly to aid digestion
- Keep a food diary to identify specific triggers that may worsen symptoms
Most patients find that post-meal diarrhea improves significantly by week 4 of treatment as the body adjusts to the medication. If symptoms persist or worsen beyond this timeframe, consult your healthcare provider about potential dose adjustments or alternative treatments.
When Ozempic Diarrhea Requires Emergency Care
While mild diarrhea from Ozempic is common and typically manageable at home, certain symptoms require immediate medical attention. Severe diarrhea can lead to serious complications, including severe dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and in rare cases, kidney problems.
Seek emergency medical attention if you experience:
- Blood in your stool or black, tar-like stools
- Fever above 101°F (38.3°C) accompanying diarrhea
- Severe abdominal pain or stomach pain that worsens or doesn’t improve
- Signs of severe dehydration, including decreased urination, dark urine, extreme thirst, dizziness, confusion, or feeling faint
- More than 10 bowel movements per day
- Diarrhea lasting longer than 4 weeks
- Sulfur burps with a rotten egg smell, combined with severe digestive symptoms
- Signs of allergic reactions, such as difficulty breathing, swelling, or hives
It’s important to note that while rare, Ozempic can potentially cause serious symptoms, including bowel obstruction. If you experience severe constipation alternating with diarrhea, inability to pass gas, or severe bloating, seek immediate medical care.
Normal, manageable diarrhea from Ozempic typically involves 3-5 loose stools daily that can be controlled with over-the-counter treatments and dietary changes. If your symptoms exceed this or if you’re concerned about your condition, don’t hesitate to contact your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Ozempic-related diarrhea, though common, is usually mild and temporary, resolving within weeks as the body adjusts. With hydration, dietary changes, over-the-counter remedies, and medical guidance when needed, patients can manage symptoms effectively. Most individuals continue treatment successfully, achieving improved blood sugar control and weight management.
The long-term benefits of Ozempic often outweigh short-term discomfort, making proactive symptom management and open communication with healthcare providers essential for sustaining treatment and overall health goals.
References
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Written by the Pandameds.com Editorial Team
Our content is created by pharmacy-trained researchers and healthcare specialists and rigorously reviewed by a diverse panel of authentic experts from the pharmaceutical and healthcare fields. This collaborative review process ensures that every article meets the highest standards of medical accuracy, reliability, and relevance.
- ✅ Authored by pharmacy-trained professionals
- 🔍 Reviewed by multiple verified experts in the pharmaceutical and healthcare niche
- 💊 Based on trusted sources including FDA, Health Canada, and peer-reviewed clinical studies
- 🔄 Regularly reviewed and updated every 90 days to maintain accuracy and trustworthiness
About Pandameds.com
Pandameds.com offers a range of weight loss medications at an affordable price.
Fast, Reliable Shipping to the USA!
Affordable Prescription Meds From Canada
Join our mailing list for exclusive promos, curated health content & more.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does Ozempic diarrhea last?
Ozempic diarrhea typically lasts an average of 3 weeks, with approximately 80% of patients experiencing resolution by week 6. At higher doses (2.0mg), symptoms may persist for 4-6 weeks. Slow dose titration can reduce symptom duration by up to 50%.
Can Ozempic cause diarrhea even at low doses?
Yes, Ozempic can cause diarrhea at the low dose of 0.5mg, affecting approximately 8% of patients. While the risk is lower than at higher doses, it is still significantly higher than placebo (2%).
Does Ozempic give you diarrhea immediately?
Diarrhea from Ozempic typically develops within one week to one month of starting treatment. The most common timeframe is during the first 2-4 weeks, particularly after starting the medication or increasing the Ozempic dose.
Why does Ozempic cause diarrhea?
Ozempic causes diarrhea through multiple mechanisms: it slows gastric emptying while potentially accelerating intestinal transit, alters gut motility, changes how the intestines absorb nutrients like sugar and fats which can irritate the intestines, and can alter the gut microbiome composition.
What is the best Ozempic diarrhea treatment?
The best treatment for Ozempic diarrhea combines multiple approaches: loperamide (Imodium) 2mg taken after each loose bowel movement, following a BRAT diet, drinking 100 ounces of water daily, and taking electrolyte solutions to prevent dehydration. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any treatment.
What should I do about Ozempic diarrhea after eating?
Post-meal diarrhea from Ozempic typically peaks 30-60 minutes after eating. To manage this, eat portions that are 50% smaller than usual, avoid trigger foods like dairy and spicy foods, wait 30 minutes after meals before physical activity, and eat slowly while chewing thoroughly.
How do I manage diarrhea while on Ozempic?
To manage gastrointestinal adverse events like diarrhea on Ozempic, combine medication (loperamide or Pepto-Bismol), dietary changes, adequate hydration, and probiotics. Monitor symptoms and contact your healthcare provider if diarrhea persists beyond 4 weeks.
Can I take Pepto-Bismol for Ozempic and diarrhea?
Yes, Pepto-Bismol (bismuth subsalicylate) can help with Ozempic diarrhea relief, especially when combined with nausea. Take 30mL after meals, but don't use it for more than 2 weeks without consulting your healthcare provider.
When is Ozempic diarrhea an emergency?
Ozempic diarrhea becomes an emergency if you experience blood in stool, fever above 101°F, severe abdominal pain, signs of severe dehydration (decreased urination, dark urine, dizziness, confusion), more than 10 bowel movements daily, or symptoms lasting longer than 4 weeks. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience these serious symptoms.
Related Blog Posts
Call Us Today!
If you have any questions, please email our support team at support@pandameds.com or call us toll-free at 1-888-862-1210.