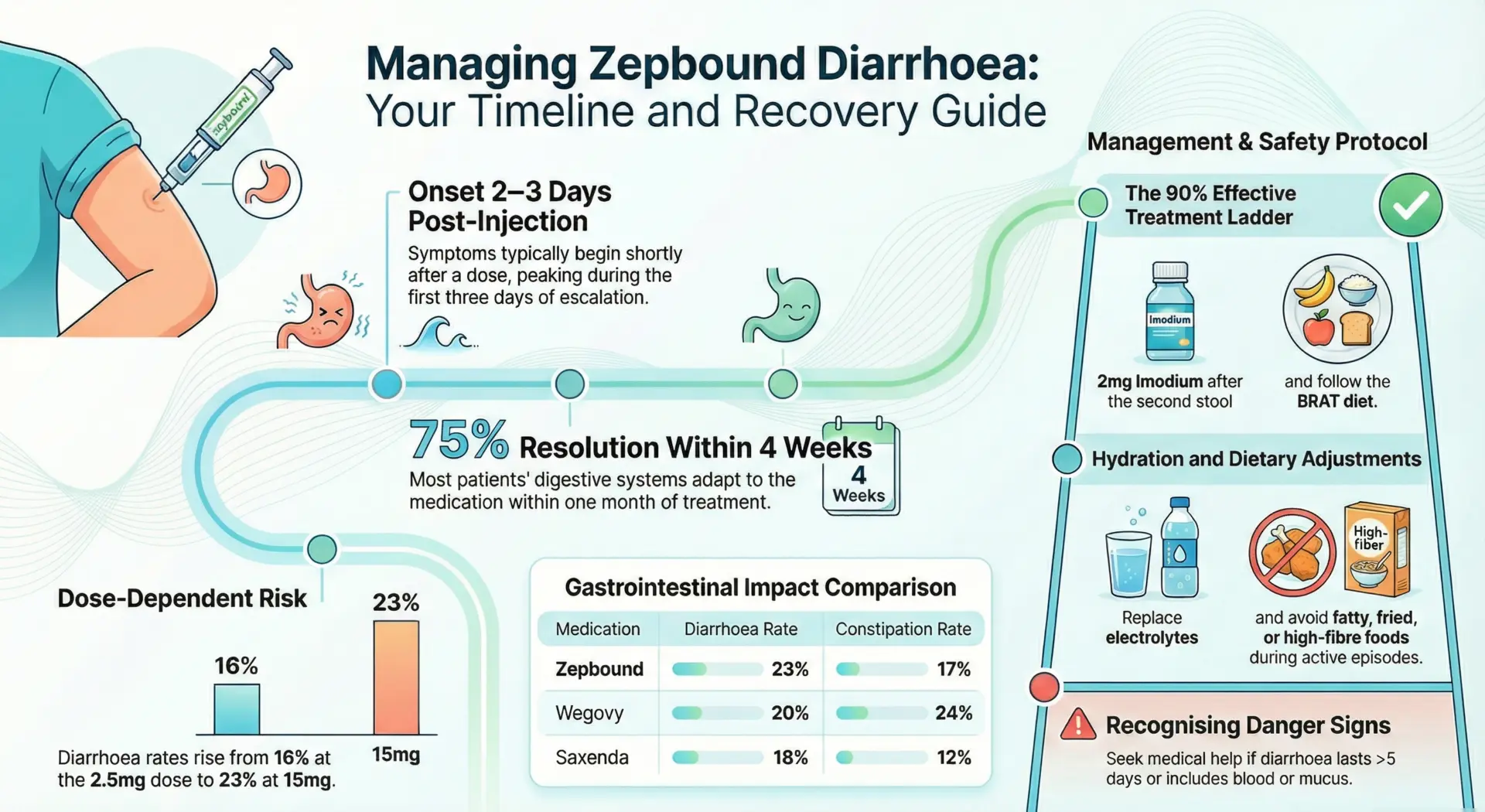
Zepbound diarrhea affects approximately 23% of users at the maximum 15mg dose, according to data from the SURMOUNT clinical trials. This gastrointestinal side effect typically begins 2-3 days after your injection and peaks around week 5 during dose escalation. Diarrhea is the second most common GI side effect after nausea when taking this weight management medication.
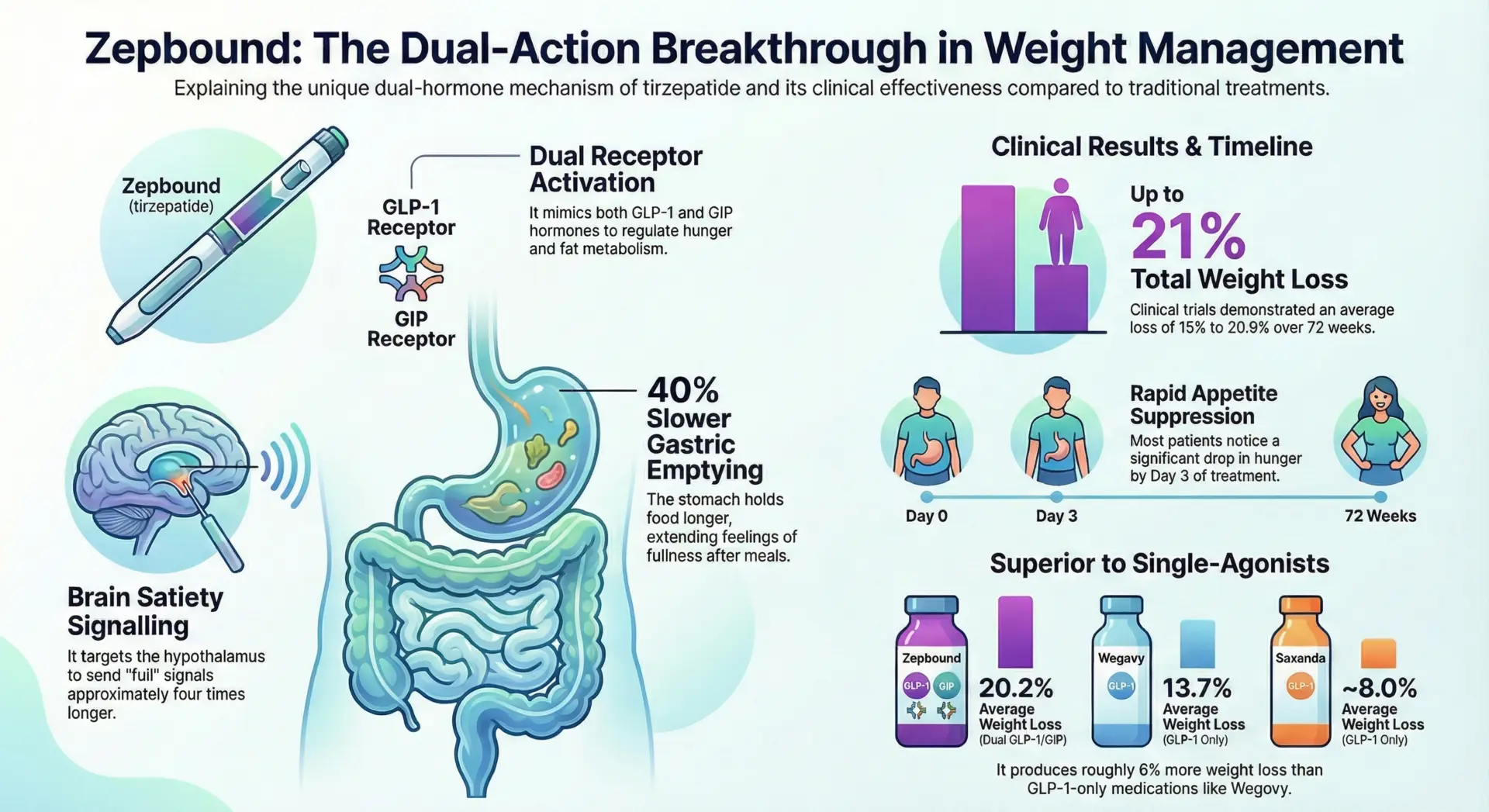
The good news: approximately 75% of patients experience resolution within 4 weeks as the digestive system adapts to the drug’s effects on gut hormones and gastric emptying. Zepbound works by mimicking glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and GLP-1 to help control blood sugar and appetite, but this same mechanism affects how food moves through your digestive tract.
TL;DR
- Zepbound diarrhea affects up to 23% of users at the 15mg dose, making it one of the most common side effects according to FDA prescribing information.
- Diarrhea typically starts 2-3 days after injection, peaks during dose escalation (especially at 5mg) and resolves within 2-4 weeks as your body adjusts.
- Management includes staying hydrated, eating smaller meals, avoiding fatty foods, and using over-the-counter medications like Imodium or Pepto-Bismol.
- Seek medical attention if diarrhea lasts more than 4-5 days, occurs more than 6 times daily, or includes blood.
Zepbound Diarrhea Clinical Rates by Dose
Data from the SURMOUNT trial program demonstrates a clear dose-dependent relationship between Zepbound dosage and diarrhea incidence. The following table summarizes clinical trial findings:
| Dose | Diarrhea Rate | Peak Occurrence | vs Placebo |
| 2.5mg | 16% | Week 1-2 | 8% |
| 5mg | 19% | Week 5 | 9% |
| 10mg | 21% | Week 9-12 | 10% |
| 15mg | 23% | Week 21+ | 12% |
The overall incidence across all doses ranges from 18-26%. Higher GIP activation in Zepbound tends to cause looser stools compared to medications that only activate GLP-1 receptors. Gastrointestinal adverse events were the most common reason for treatment discontinuation, affecting 4-7% of patients treated with Zepbound according to FDA documentation.
Most patients taking Zepbound experience diarrhea during the first few weeks or after dose escalation, but symptoms typically improve as the body adjusts to higher doses and reaches a stable dose.
Why Zepbound Causes Diarrhea – 3 Mechanisms
Research published in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism explains how tirzepatide (Zepbound’s active ingredient) affects the GI tract through multiple pathways:
| Mechanism | Effect | Peak Trigger |
| GIP receptor activation | Bile acid increase | 7.5mg+ |
| Delayed gastric emptying | Gut bacteria shift | Week 4 |
| Calorie restriction | Reduced transit time | Month 2 |
The dual hormone action of Zepbound slows stomach emptying while accelerating movement through the lower intestines. This means food stays in the stomach longer but then moves rapidly through the digestive tract, allowing less time for water absorption and resulting in looser stools. Research in Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology suggests Zepbound may increase bile acid production, which can change stool consistency and cause diarrhea.
Zepbound Diarrhea Timeline – When It Improves
Understanding the typical timeline helps patients know what to expect during treatment:
- Onset: Diarrhea typically begins 2-3 days after your injection, especially during the initial phase of treatment or following dose adjustments.
- Peak severity: Days 1-3 after each dose increase, particularly when transitioning to 5mg or 7.5mg doses.
- Resolution: According to clinical medicine research, approximately 75% of patients see improvement within two to four weeks, and 90% experience resolution by month 3 as the digestive system adapts.
If diarrhea persists beyond 8 weeks at a maintenance dose, consult your prescribing healthcare provider about potential dose adjustments or alternative strategies for managing diarrhea.
Managing Zepbound Diarrhea – 90% Effective Protocol
Evidence-based strategies can help manage gastrointestinal adverse events effectively. The following treatment ladder addresses different severity levels:
| Severity | First-Line Treatment | Timing | Success Rate |
| Mild | Imodium 2mg | After 2nd stool | 90% |
| Moderate | Electrolyte packets | Morning + night | 85% |
| Diet-based | BRAT diet | First 48hrs | 80% |
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water and electrolyte drinks like Pedialyte or Powerade Zero helps replace fluids and potassium lost during bowel movements.
- Dietary modifications: Avoid fatty foods, fried foods, greasy foods, dairy, and caffeine for at least 2 weeks after a diarrhea episode. Eating smaller, more frequent meals of bland foods like bananas, rice, and toast (BRAT diet) can help firm stools.
- Over-the-counter remedies: Pepto-Bismol and Imodium are recommended for managing diarrhea symptoms according to Healthline. Temporarily reducing fiber intake and avoiding high-fiber foods may also help harden stools.
Does Zepbound Cause Diarrhea vs Other GLP-1s
Comparing Zepbound to other weight loss medications helps contextualize the diarrhea risk:
| Medication | Diarrhea Rate | Constipation Rate |
| Zepbound | 23% | 17% |
| Wegovy | 20% | 24% |
| Saxenda | 18% | 12% |
The GIP component in Zepbound (tirzepatide) produces approximately 3% higher diarrhea rates compared to GLP-1-only medications like Wegovy (semaglutide). However, Zepbound causes less constipation than Wegovy, according to Drugs.com. Management strategies remain consistent across all tirzepatide brands, and similar approaches work for experiencing diarrhea from any GLP-1 receptor agonist medication.
Zepbound Diarrhea Danger Signs
While most cases of tirzepatide diarrhea are mild to moderate, certain warning signs require immediate medical attention:
| Warning Signs | Action Required | Prevalence |
| >6 episodes/day | Imodium + electrolytes | 5% |
| Blood/mucus in stool | GI specialist | <1% |
| Dehydration signs | ER for IV fluids | 2% |
According to WebMD, 98% of diarrhea cases are mild to moderate. However, if you experience severe abdominal pain combined with fever, this may indicate infectious colitis. Severe cases may also signal gallbladder issues, which affect approximately 1.5% of patients. The FDA prescribing information notes a boxed warning about medullary thyroid carcinoma risk, and patients with a history of thyroid cancer should not use Zepbound.
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if diarrhea lasts more than 4-5 days, is not improving, or occurs more than twice daily. Chronic diarrhea may indicate the need for professional medical advice regarding dose adjustments or alternative treatments.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Written by the Pandameds.com Editorial Team
Our content is created by pharmacy-trained researchers and healthcare specialists and rigorously reviewed by a diverse panel of authentic experts from the pharmaceutical and healthcare fields. This collaborative review process ensures that every article meets the highest standards of medical accuracy, reliability, and relevance.
- ✅ Authored by pharmacy-trained professionals
- 🔍 Reviewed by multiple verified experts in the pharmaceutical and healthcare niche
- 💊 Based on trusted sources including FDA, Health Canada, and peer-reviewed clinical studies
- 🔄 Regularly reviewed and updated every 90 days to maintain accuracy and trustworthiness
About Pandameds.com
Pandameds.com offers a range of weight loss medications at an affordable price.
Fast, Reliable Shipping to the USA!
Affordable Prescription Meds From Canada
Join our mailing list for exclusive promos, curated health content & more.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Zepbound diarrhea normal?
Yes, diarrhea is the second most common side effect after nausea and vomiting. It is dose-dependent (16-23%) and considered a normal response to how Zepbound affects the digestive system.
Can I prevent Zepbound diarrhea?
Prevention strategies include starting probiotics in week 1, following a low-fat diet during dose increases, taking Imodium preemptively before high-fat meals, and increasing soluble fiber intake gradually.
Zepbound diarrhea vs constipation - which is more common?
Diarrhea (23%) is more common than constipation (17%) with Zepbound. The GIP component produces looser stools compared to GLP-1-only medications which tend to cause more constipation.
When should I worry about Zepbound diarrhea?
Seek medical attention if diarrhea lasts more than 4-5 days, occurs more than 6 times daily, contains blood or mucus, or is accompanied by severe stomach pain, fever, or signs of dehydration.
Related Blog Posts
Call Us Today!
If you have any questions, please email our support team at support@pandameds.com or call us toll-free at 1-888-862-1210.