Metformin hydrochloride is the preferred first-line medication for managing blood sugar control in adults with type 2 diabetes, according to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) Standards of Care.
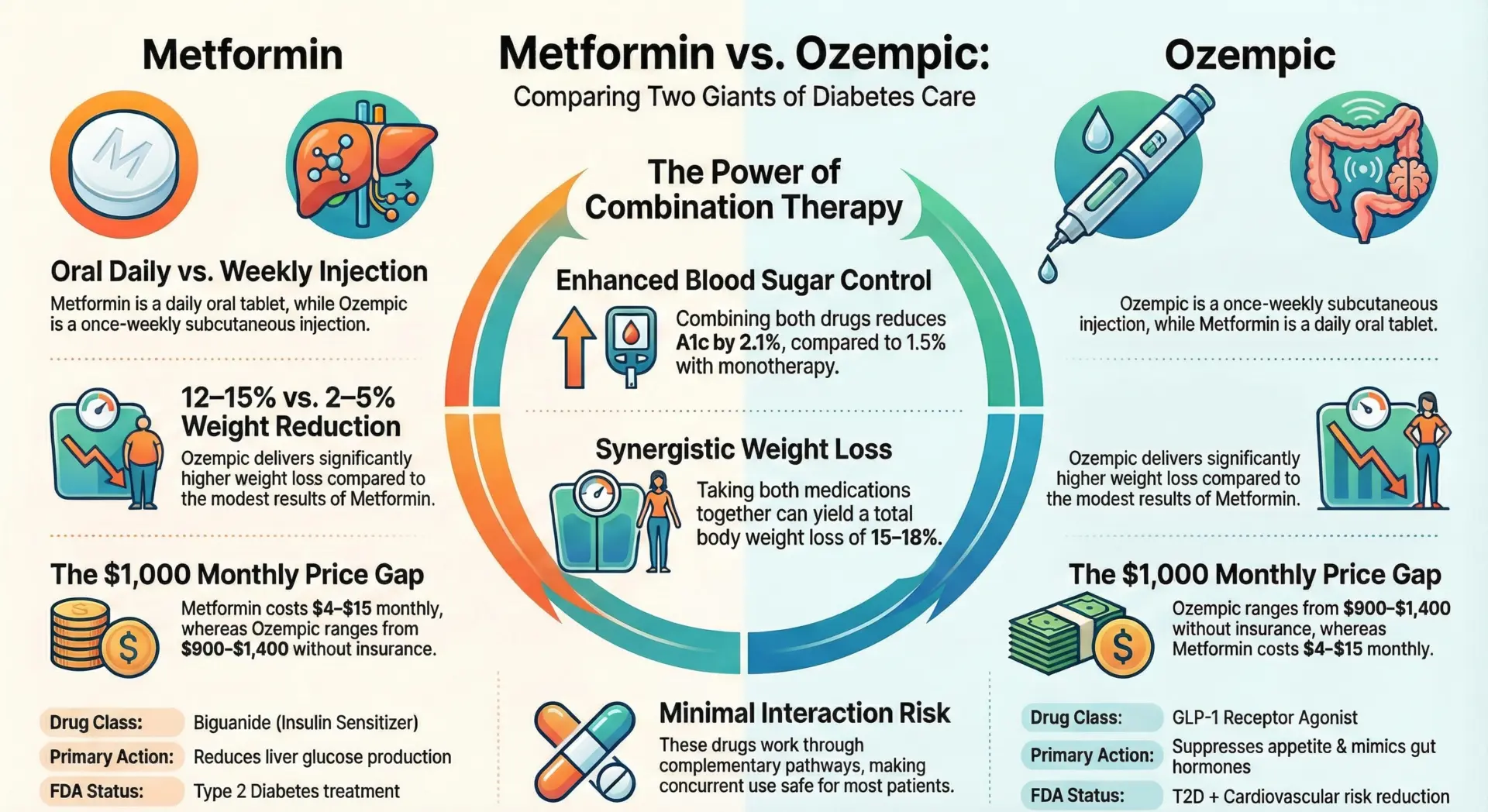
As an active drug in the biguanide class, metformin works by reducing hepatic glucose production, improving insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues, and lowering blood glucose levels without directly stimulating the pancreas to produce insulin. This makes it a cornerstone of diabetes management that can also support modest weight loss and improved glycemic control.
Below is a complete guide to metformin dosing across all major use cases covering standard diabetes therapy, weight loss, prediabetes prevention, and special population adjustments backed by current clinical evidence and prescribing guidelines from the FDA prescribing information for metformin.
TL;DR
- Metformin dosing depends on formulation and indication.
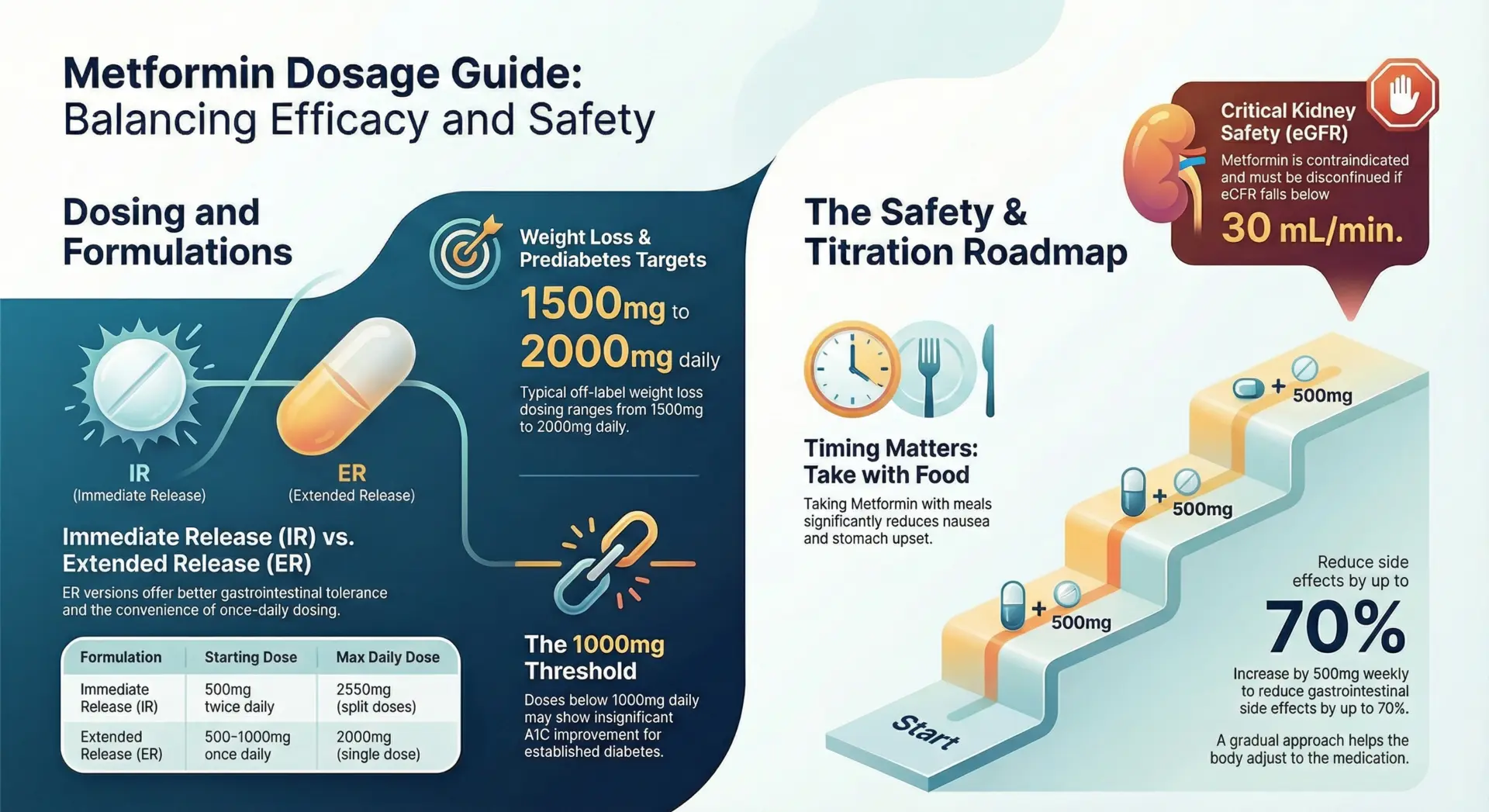
- For type 2 diabetes, the standard starting dose of metformin is 500 mg taken orally twice a day (immediate-release) or 500-1000 mg once daily with the evening meal (extended-release).
- The maximum daily dose is 2550 mg for IR and 2000 mg for ER formulations. For weight loss in non-diabetics, 1500-2000 mg daily is the typical off-label target.
- For prediabetes, 500-850 mg daily can reduce progression to diabetes by up to 31%.
- Always titrate slowly adding 500 mg weekly to minimize gastrointestinal side effects.
- Patients with kidney disease or renal impairment require dosage adjustments based on eGFR levels, and metformin is contraindicated when eGFR falls below 30 mL/min due to the risk of lactic acidosis.
- Consult your healthcare providers before starting or changing any dose of metformin.
Standard Metformin Dosage Chart: IR vs ER
The table below summarizes the recommended metformin dosage chart for adult patients with diabetes mellitus. All metformin doses should be taken with meals to reduce upset stomach and improve absorption, as noted in the FDA-approved labeling.
| Form | Starting Dose | Titration | Maintenance | Max Daily |
| Immediate Release (IR) | 500mg 2x/day or 850mg 1x/day | +500mg weekly | 1500-2000mg | 2550mg (850mg 3x) |
| Extended Release (ER) | 500-1000mg 1x evening | +500mg weekly | 1500mg | 2000mg 1x |
When to take: All doses should be taken with meals typically breakfast and dinner for IR, or with the evening meal for ER. Taking metformin with food reduces gastrointestinal side effects by approximately 70%, according to clinical practice data.
Responses at doses below 1000 mg daily may produce clinically insignificant A1C improvement for established diabetes. The maintenance dose of 2000 mg per day in divided doses is considered optimal for most adults.
For pediatric patients aged 10 years or older, the initial dose is 500 mg orally mg twice daily, with a maximum dose of 2000 mg per day. Metformin dosing for children follows the same slow titration approach used in adults, as recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Is 500mg of Metformin a Low Dose?
Yes, 500 mg is considered a low, starter-level dose of metformin. Physicians prescribe this lower dose during week one to allow the body to adjust and minimize gastrointestinal side effects such as diarrhea, nausea, and upset stomach. Clinical experience shows that starting at 500 mg rather than higher doses reduces the incidence of diarrhea from roughly 30% down to about 10%.
Weight loss context: At just 500 mg daily, patients typically experience only 2-3% body weight reduction, compared to 5-7% at 1000 mg to 1500 mg or more. For those using metformin specifically for weight loss, 500 mg alone is generally insufficient for meaningful appetite control and fat reduction. The appetite metallic taste that some patients notice may mildly suppress intake, but the primary metabolic benefits require higher doses.
Prediabetes: However, for prediabetes prevention, 500 mg may be adequate. The landmark Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP) trial demonstrated that metformin therapy reduced progression to type 2 diabetes by 31% versus placebo over approximately three years and lower doses played a meaningful role alongside lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise.
Metformin Maximum Dose Per Day: 2550mg IR / 2000mg ER
The maximum daily dose of metformin depends on the formulation:
- Immediate-release (IR): The maximum dose is 2550 mg per day, taken as 850 mg three times daily with meals. When exceeding 2000 mg daily, dividing into three divided doses is essential for tolerability and to help lower blood sugar evenly throughout the day.
- Extended-release (ER): The maximum dose is 2000 mg once daily, taken with the evening meal. The metformin extended release tablets offer better GI tolerance compared to IR.
Overdose and safety: Taking too much metformin can cause serious complications. Early signs include severe nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain. In severe cases, overdose can trigger lactic acidosis a buildup of too much lactic acid in the blood causing metabolic acidosis (specifically, anion gap acidosis).
Metformin carries a black box warning from the FDA for this risk. Patients with an eGFR below 30 mL/min are contraindicated due to the elevated risk of developing lactic acidosis.
Metformin Dosage for Weight Loss: Non-Diabetics
Metformin is not FDA-approved for weight loss, but it is increasingly prescribed off-label for this purpose, particularly in individuals with insulin resistance, polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), or a BMI above 30. The following table outlines typical dosing strategies used in clinical practice for weight loss in non-diabetic individuals:
| Goal | Dose | Expected Loss | Duration |
| Non-Diabetic Weight Loss | 1500-2000mg daily | 5-8% in year 1 | Off-label, ongoing |
| 500mg Starter (tolerance test) | 500mg 2x/day | 2-3% | 2-4 weeks |
| Maximum Effect (BMI >30) | 2000mg ER | ~7% sustained | 12+ months |
For non-diabetic patients, 500 mg alone is typically too low for significant appetite suppression. Most clinicians target 1500 mg in split doses for meaningful effects on appetite control and blood glucose regulation. Metformin helps reduce cravings by improving insulin signaling and can lead to decreased appetite over time.
In premenopausal women with PCOS, some practitioners recommend a slightly lower ceiling of approximately 1700 mg due to eGFR variance. Metformin in PCOS also improves ovulatory function and metabolic markers, as discussed in Endocrine Society clinical guidelines.
Any off-label use for weight management should be combined with lifestyle changes including diet and exercise for best results.
Lowest Dose of Metformin: 500mg Starting
The absolute lowest commercially available and clinically studied dose of metformin is 500 mg once daily. This is the standard starting point for prediabetes management, gestational diabetes (off-label), and patients who are highly sensitive to gastrointestinal effects.
Doses below 500 mg (such as splitting a 500 mg tablet into 250 mg) have not been adequately studied in clinical trials and are considered subtherapeutic for meaningful A1C reduction. There is no established evidence supporting doses below 500 mg for blood sugar control or any other indication. The FDA prescribing information lists 500 mg as the minimum recommended dose.
Metformin Dosage for Prediabetes
The ADA Standards of Care 2026 recommend considering metformin for adults with prediabetes, particularly those with a BMI above 35 kg/m², those under age 60, or premenopausal women with a history of gestational diabetes. The typical metformin starting dose for prediabetes is 500 mg once daily, increasing to 850 mg daily if A1C levels remain above 5.7% after three months.
Long-term data from the DPP Outcomes Study showed that metformin at 850 mg twice daily for approximately three years prevented 31% of T2D progression compared to placebo though this benefit was smaller than the 58% reduction achieved through intensive lifestyle changes. For prediabetes, metformin serves as an adjunct to diet and exercise rather than a replacement, and the dose is typically kept lower than what is used to treat diabetes.
Metformin ER Dosage Advantages
Metformin extended release tablets offer several practical advantages over immediate-release formulations. The primary benefit is convenience: ER allows a same total daily dose to be taken as a single mg once daily dose with the evening meal, rather than splitting into two or three doses throughout the day.
GI tolerability is also significantly improved. Clinical data suggest that diarrhea rates are approximately 15% with ER compared to 45% with IR at equivalent doses. For patients who cannot tolerate IR formulations due to persistent nausea, stomach pain, or diarrhea, the standard recommendation is to switch to ER at the same total daily dose. For example, a patient taking 1000 mg IR mg twice daily would switch to 2000 mg ER once daily.
Titration Schedule: Slow Ramp Prevents 80% of GI Issues
Gradual dose escalation is the single most effective strategy to minimize gastrointestinal side effects when starting metformin. The following titration protocol is recommended by most healthcare providers:
- Week 1: Start with 500 mg once or twice daily with meals. This allows the body to adjust and identifies patients who are highly sensitive.
- Weeks 2-3: Increase by 500 mg per week as tolerated. Move to 1000 mg daily (split as mg twice daily for IR, or mg once daily for ER), then to 1500 mg.
- Week 4 onward: Reach the target maintenance dose of 1500-2000 mg daily. Continue monitoring for side effects, including decreased appetite, nausea, and muscle pain.
Kidney adjustment
Patients with reduced renal function require modified targets. With an eGFR of 45-60 mL/min, the maximum dose should not exceed 2000 mg daily.
If eGFR falls below 45 mL/min, the daily dose should be reduced by 50%, and if eGFR drops below 30 mL/min, metformin should be discontinued entirely to prevent kidney failure complications and lactic acidosis. These guidelines are outlined by the FDA and the National Kidney Foundation.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Written by the Pandameds.com Editorial Team
Our content is created by pharmacy-trained researchers and healthcare specialists and rigorously reviewed by a diverse panel of authentic experts from the pharmaceutical and healthcare fields. This collaborative review process ensures that every article meets the highest standards of medical accuracy, reliability, and relevance.
- ✅ Authored by pharmacy-trained professionals
- 🔍 Reviewed by multiple verified experts in the pharmaceutical and healthcare niche
- 💊 Based on trusted sources including FDA, Health Canada, and peer-reviewed clinical studies
- 🔄 Regularly reviewed and updated every 90 days to maintain accuracy and trustworthiness
About Pandameds.com
Pandameds.com offers a range of weight loss medications at an affordable price.
Fast, Reliable Shipping to the USA!
Affordable Prescription Meds From Canada
Join our mailing list for exclusive promos, curated health content & more.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Metformin Maximum Dose Per Day?
The maximum daily dose is 2550 mg for immediate-release formulations (typically 850 mg taken three times daily) and 2000 mg for extended release formulations taken mg once daily. Always take all doses with meals and under the supervision of healthcare providers.
Is 500mg Metformin a Low Dose for Weight Loss?
Yes, 500 mg is a starter dose for weight loss that typically results in only 2-3% body weight reduction. For meaningful weight loss results (5-7%), most practitioners target a dose of 1500 mg or higher, combined with lifestyle changes and regular exercise.
What Is the Metformin Dose for Weight Loss in Non-Diabetics?
Non-diabetic patients are typically prescribed 1500-2000 mg daily in split doses with meals. This is an off-label use, and consultation with a physician is essential. Patients with insulin sensitivity issues, such as those with PCOS, may start at a lower dose and titrate up.
What Is the Lowest Dose of Metformin?
The lowest standard dose is 500 mg once daily. This is the minimum studied dose for prediabetes and the typical starting point for all patients new to metformin.
What Is the Metformin Starting Dose?
The standard metformin starting dose is 500 mg taken once or twice daily with food. Doses are titrated upward by 500 mg weekly until reaching the target maintenance dose, typically 1500-2000 mg daily for type 2 diabetes or weight loss indications.
Related Blog Posts
Call Us Today!
If you have any questions, please email our support team at support@pandameds.com or call us toll-free at 1-888-862-1210.